Irrelevant Topics V
in Physics
Topics:
Random Matrix Theory
Physics, Mathematics
Complex Temperatures
Physics
Stochastic Resonance
Physics
Random Matrix Theory
when the average is too much information
What do you know, really?
Each branch of physics makes certain assumptions and simplifications. Break it down on what is known
- Classical - Exact:
- Quantum - Exact in a probable sense:
- Fluid Mechanics - Averaged:
- Statistical Mechanics - Ensemble averaged:
- Random Matrix Theory - Ensemble only:
Ensemble only?
How could this possibly be useful?First formally studied in physics by Wigner (yes that one) via detailed atomic models. Eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian would give the energies but Wigner supposed that the exact numbers entries do not matter per se. The ensemble from which they are chosen from should have the same statistics, thus "average" predictions should be correct. Choose an ensemble of matrices that have the same symmetries as your system.
Ensembles of matrices?
GOE (Gaussian orthogonal ensemble) probability density:
product of differentials of the independent matrix elements, matrix size, Gaussian factor introduced to render integrals over space convergent (cutoff). Characterized by a single parameter , with dimensions of energy, Determines the mean-level spacing.
Look at statistics of eigenvalues : Nearest neighbor spacing
Typical Spacings for different systems
Wigner and Girkos Law
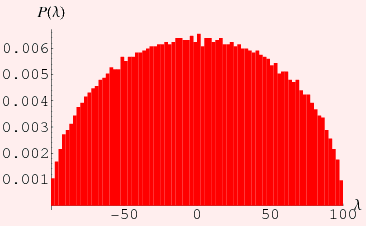
Eigenvalue spacing for a Real (Symmetric)
Matrix whose entries are from a Standard Normal Distribution
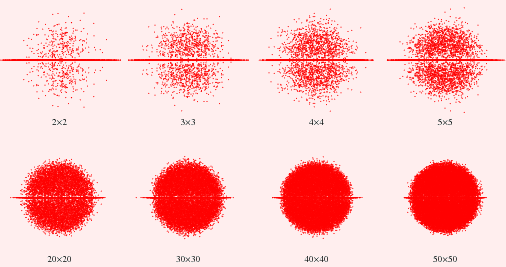
Girko's Law predicts eigenvalues spacing
will cover the unit disc uniformly.
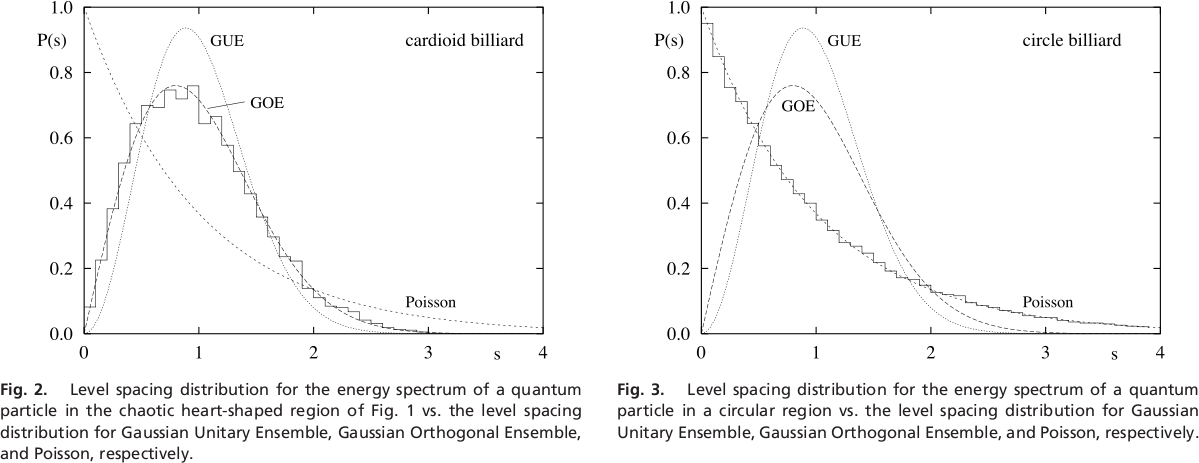
Quantum Chaos
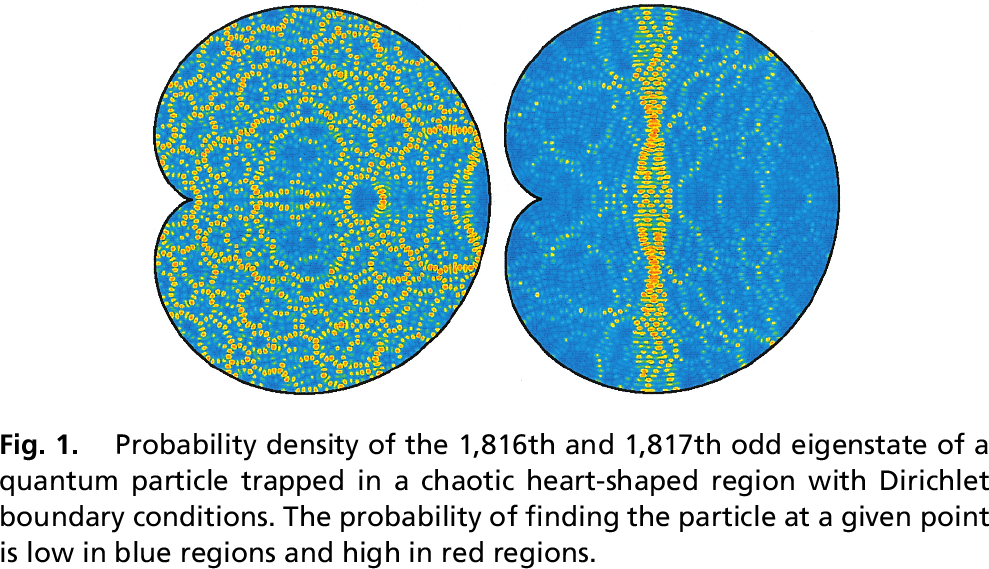
Quantum Chaos
as a function of Integrability
Bonus!
Connections to Riemann-Zeta function
One of the most famous functions in mathematics:
Complex Temperatures
Is it hot in here or am I imagining things?
Since Stat. Mechanics. was too easy
Motivation comes from the theory of phase transitions:
Phase transitions occur where the free-energy is non-analytic. Make the substitution (Yang-Lee) or (Fisher). has complex roots, which in the thermodynamic limit , may collapse onto the real axis. If a root does lie on the real axis then phase transition will occur! This can NOT happen in finite systems! One can use renormalization, and finite-size scaling tricks to find the critical points.
Cayley Tree
(aka) Beethe Lattice
As a sample system, look at the Ising Bethe lattice:
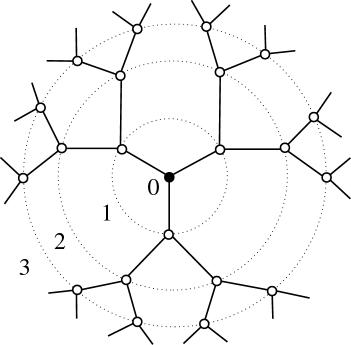
Often times this model is exactly solvable for a given .
Surface area Number of nodes (very unusual!)
Fractal when
Yang-Lee partition function zeros for the Ising Cayley tree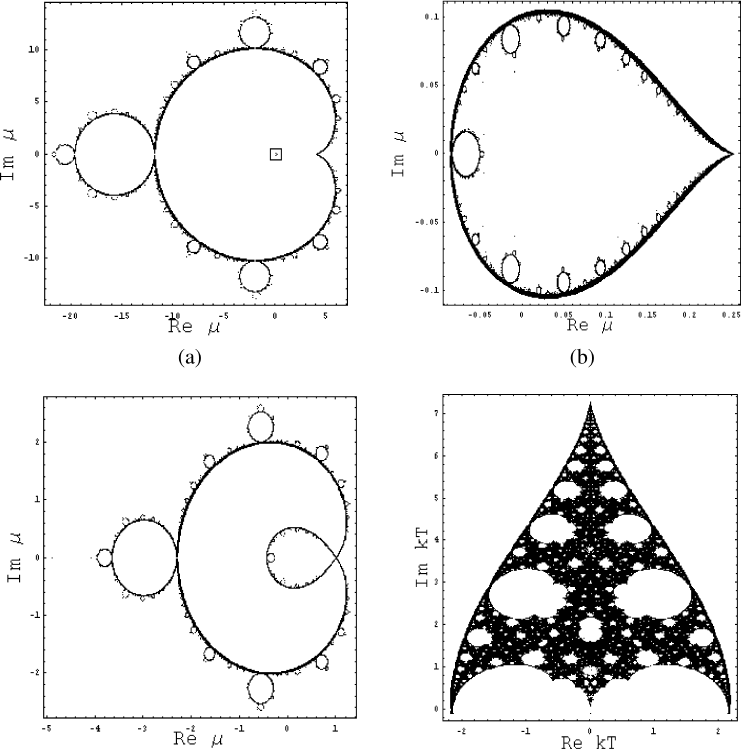
om-nom-nom
Fisher partition function zeros for the Ising Cayley tree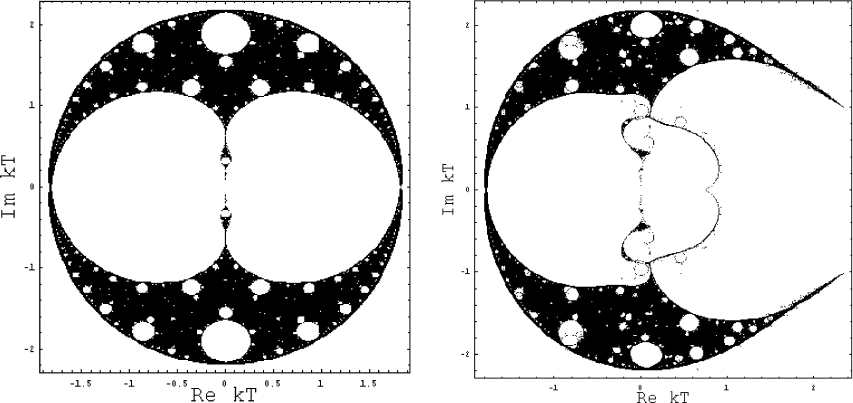
YL and Fisher Zeros
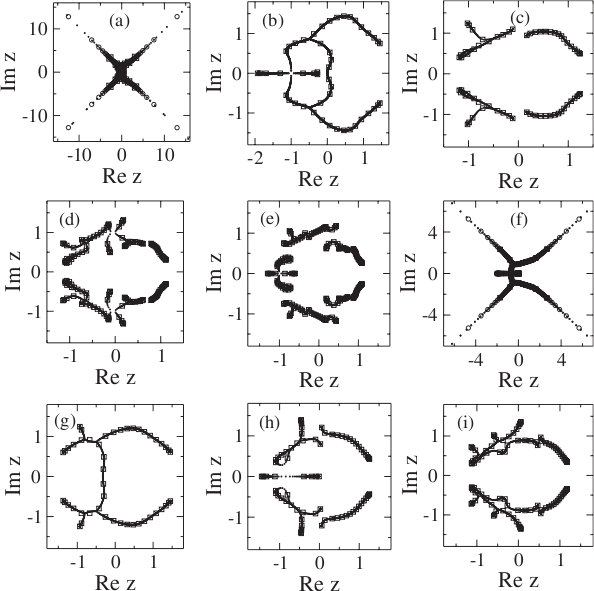
Partition function zeros for one-dimensional Blume-Capel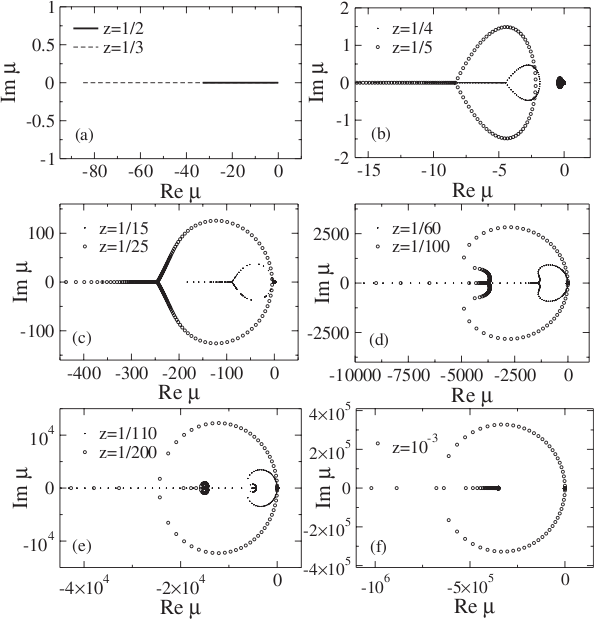
Stochastic Resonance
when messy is good
Nonlinear system where noise helps otherwise weak signal induce transitions between stable equilibrium states.
Started with studies of ice-age periodicity.
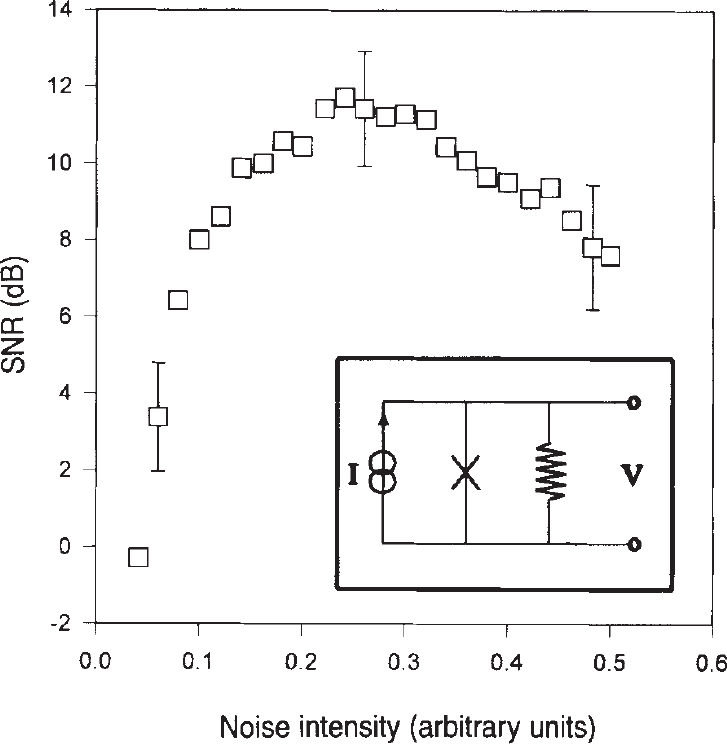
Applicable to Schmitt riggers, ring-laser experiments, neurological inputs, Josephson Junctions and more...
Simplest example of Stochastic Resonance
Overdamped Brownian motion in bistable
potential with periodic forcing:
is a Wigner process, i.e. white, Gaussian noise. Function has two peaks at . In absence of forcing fluctuates around local minima according to Kramer's rate:
At resonant values of the "signal" (i.e. the value that can be detected from the noise) is at maximized:
SR: Example Potential
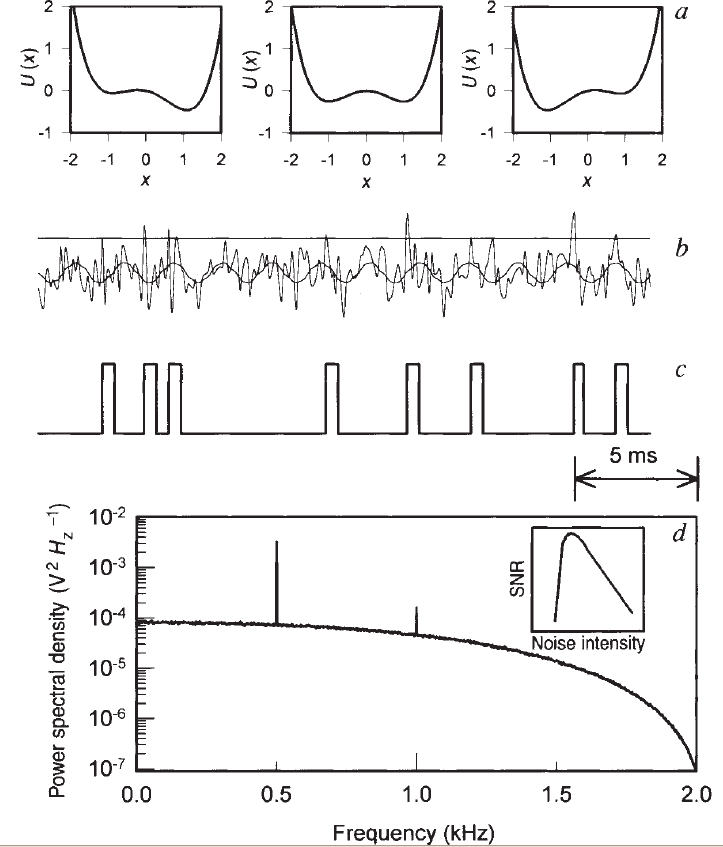
Physical SR: Josephson Junctions