Enhancing the coevolutionary signal.
Travis Hoppe
NIH/NIDDK/LCP Postdoctoral Fellow
Outline
Alignment / coevolution
Score functions
Structure prediction
Sequence to structure prediction
Sequence Multiple Sequence Alignment ...DTSGVQGIDVSHWQGSINWSSVKSAGMSFAYIKATEGTNYKDDRFSANYTNAYNAGIIRGAYHFARPNASSGTAQADYFASNGGGWSRDNRTLPGVLDIEHNPSGAMCYGLSTTQMRTWINDFHARYKARTTRDVVIYTTASWWNTCTGSWNGMAAKSPFWVAHWGVSAPTVPSGFPTWTFWQYSATGRVGGVSGDVDRNKFNGSAARLLALANNTA
----DYGIDVSSSTSQSQWSCLAGKN-QRAIIQVWSGGYGLNSQASSIISAAKSAGFQVDVYAFLCNQCSPSSNVIQQIVNSL---GGQFGT--LWIDVEQCS---GCWG-DVNDNAAFVAEAVQTAAS-LGVTVGVYSSLGEWPQTVGSL-SSLSSYPQWYAHYDGVAASQYGGWDNPEMKQYVGNTNECGV--SVDLDYYG--------------
----ELGIDVSSATSQSQWSCLAQKN-QRAIIQVWSGGYGMNNGVVSAIQAAQNAGFQVDLYAFLCNQCSPSSNVIQQIVSKIKQSGVSFGT--LWIDVEQCS---GCWG-STSANAAFVVEAVQTAAS-LGVRVGVYSSSGEWPQTVGTL-TSLSSYPQWYAHYDGVPAGQYGGWNNPEMKQYVGNTNQCGV--SVDLDFYG--------------
----TYGVDL------AGFQCLVGKGF-FAIVRCYMSSGGIDPNCASSVSAAWAGGMTVDLYLFPCFSCG----SLVQFAQS---NGVNFGK--IWLDIEGPG---TYWG-DQGANQQFFEGLVQGL--S-GVSVGIYTSESQWSPIMGDY-SGGSNFPLWYANYDGSPN-PFGGWSTPTMKQFDDPSN-CGI--GIDENWIG--------------
----GTGIDISSPTSKTQWSCLAKQN-TKAIIQVWSGGYGYNTNIASSVSAAKSAGIQVDLYAFLCSQCSPSSSAIKTLVSNLRSQNVEFGT--LWIDVEQCS---NCWG-STSTNAQFVVEAVQTAQQ-LGVSVGVYSSIGEWSQTVGSL-NSLSSFPLWYAHYDNVPASQFGSWSSPAMKQYAGNTQQCGV--SVDLDFFQ--------------... Contact maps Structure
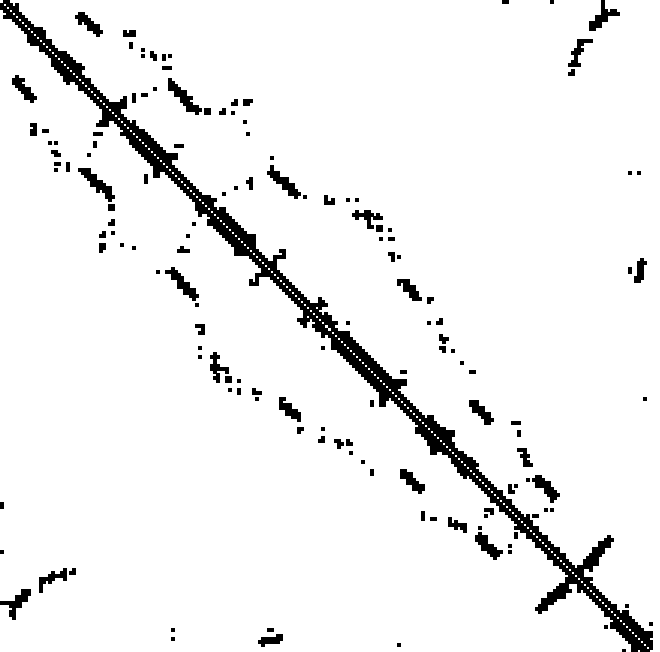

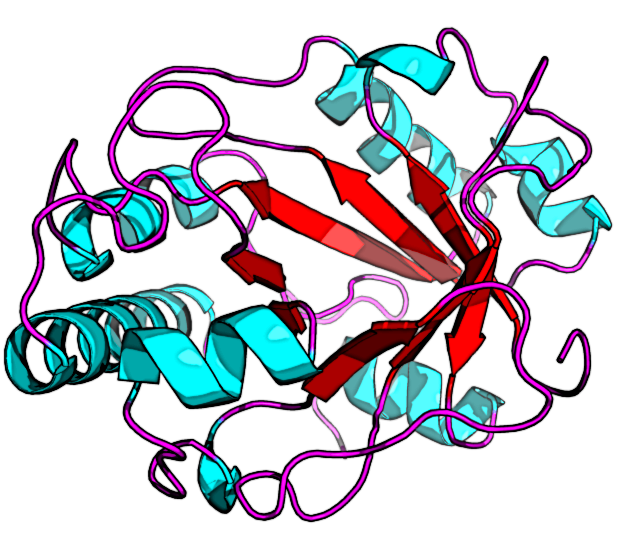
What is coevolution?
Observation: Homologous proteins impose strong constraints
on their sequence variability.
Assume: If two residues form a contact, a destabilizing substitution at one position is expected to be compensated by a substitution of the other position over the evolutionary timescale, in order for the residue pair to maintain attractive interaction.
Mutual information
(naïve attempt)
are observed frequencies and co-frequencies respectively.
works poorly due to transitivity. e.g. A-B and B-C, this model predicts A-C.
Maximum-entropy model / Markov Random Field
Least-constraint model that matches marginal distributions of and .Brute force computational complexity of pairwise is .
Learned parameters
encodes individual propensity of each amino acid at positionstatistical coupling of amino acid propensities between positions
DCA (direct coupling analysis)*
Focus on high MI pairs, use reduced two-residue systems.
PSICOV
Compute pairwise covariance over all pairs of sites for all residues from MSA. Invert the matrix with tricks to avoid singular matrices (assume sparsity, most entries are zero in inversion).
GREMLIN
Optimize the pseudolikelihood of Models conditional distribution of the original joint distributioninstead of the joint distribution itself. Can add regularization
to prevent overfitting and prior knowledge.
encodes individual propensity of each amino acid at position
statistical coupling of amino acid propensities between positions
Target dataset
Pfam families with sequences with high resolution .
150 monomeric proteins residues; diverse set.
PDB-ID Pfam-ID Nseq Length Description
========================================================================================
1GUUA PF00249 10393 50 Myb-like DNA-binding domain
1BRFA PF00301 1430 53 Rubredoxin
1AAPA PF00014 2256 56 Kunitz/Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor domain
1JO8A PF00018 6287 58 SH3 domain
1KU3A PF04545 8439 61 Sigma-70, region 4
1M8AA PF00048 1062 61 Small cytokines (intecrine/chemokine), interleukin-8 like
1C9OA PF00313 6807 66 'Cold-shock' DNA-binding domain
1VFYA PF01363 1645 67 FYVE zinc finger
1CTFA PF00542 2390 68 Ribosomal protein L7/L12 C-terminal domain
1KW4A PF07647 1192 70 SAM domain (Sterile alpha motif)
1CC8A PF00403 9383 72 Heavy-metal-associated domain
1ATZA PF00092 7567 75 von Willebrand factor type A domain
1TIFA PF05198 1947 76 Translation initiation factor IF-3, N-terminal domain
1H98A PF00037 10421 77 4Fe-4S binding domain
1T8KA PF00550 20685 77 Phosphopantetheine attachment site
1BDOA PF00364 11826 80 Biotin-requiring enzyme
1AVSA PF00036 13234 81 EF hand
1CXYA PF00173 3200 81 Cytochrome b5-like Heme/Steroid binding domain
1I71A PF00051 1082 83 Kringle domain
1ABAA PF00462 5749 87 Glutaredoxin
1DSXA PF02214 1372 87 K+ channel tetramerisation domain
1SMXA PF10150 2203 87 Ribonuclease E/G family
1NPSA PF00030 1153 88 Beta/Gamma crystallin
1PCHA PF00381 3344 88 PTS HPr component phosphorylation site
1VJKA PF02597 3283 88 ThiS family
1FNAA PF00041 17137 91 Fibronectin type III domain
1G9OA PF00595 14944 91 PDZ domain (Also known as DHR or GLGF)
1FK5A PF00234 3346 93 Protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family
Data pipeline
Download, parse, and clean PDB.
Build FASTA and reference contact map.
Align each FASTA using HHBLITS*.
Score alignments with GREMLIN.
Build contact maps from GREMLIN.
(optional) Optimize contact map score with RF.
Fold coarse-grained protein from contact map.
hhblits -i input.seq -n 4 -diff inf -cov 75 -e 0.0000000001 Dockerize GREMLIN's MATLAB for maximum performance.
Scoring
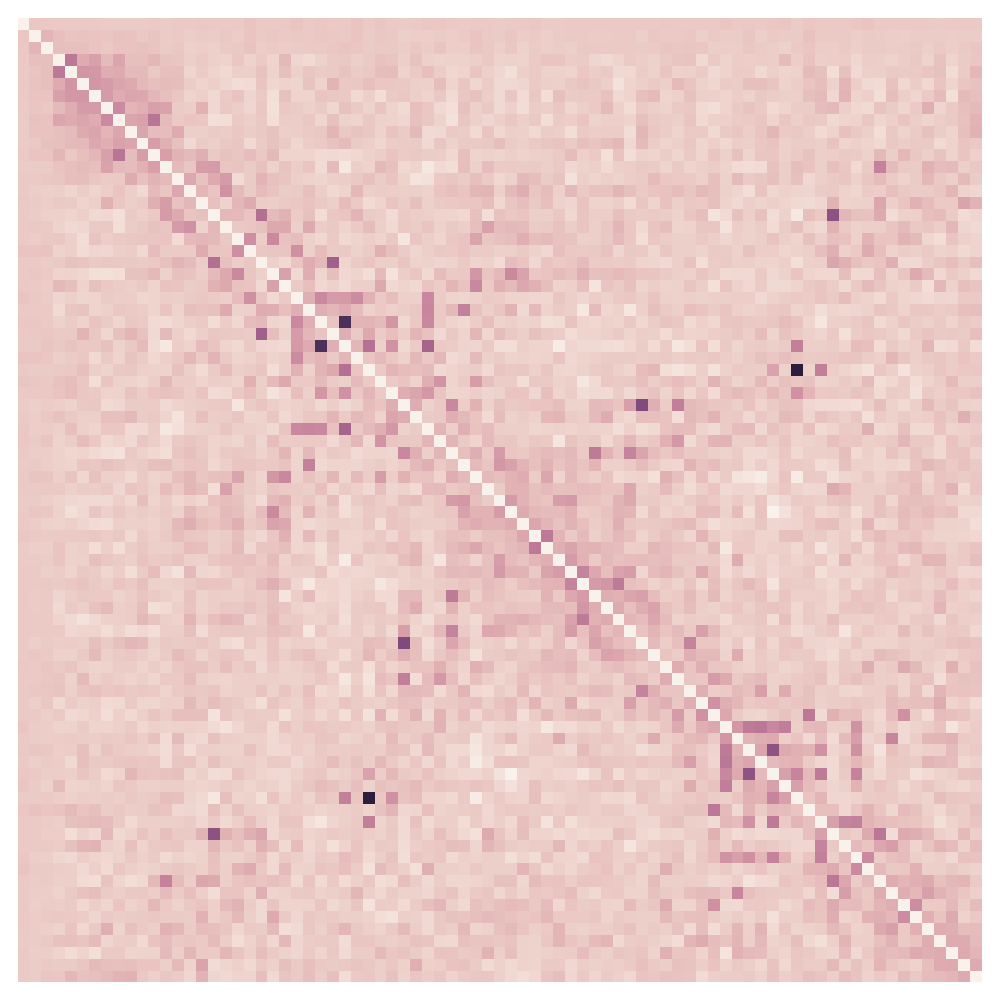
For a given protein and alignment GREMLIN gives tensor.Reduce GREMLIN's tensor output:
Drop information about gaps.Compute the Frobenius norm over each position.
Subtract average product correlation*, structural vs. shared ancestry
Top score model
Rank sort top diagonal of , take top contacts.Typically values for .
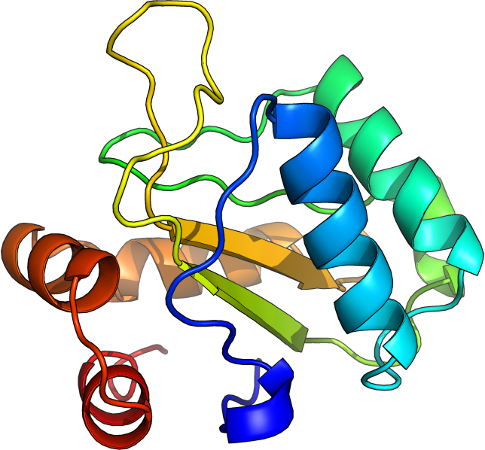
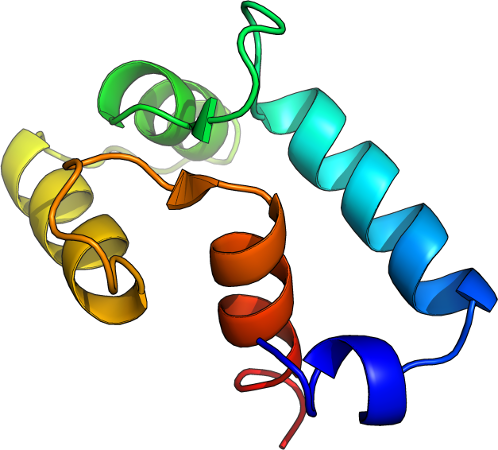
Example proteins, GREMLIN APC corrected score
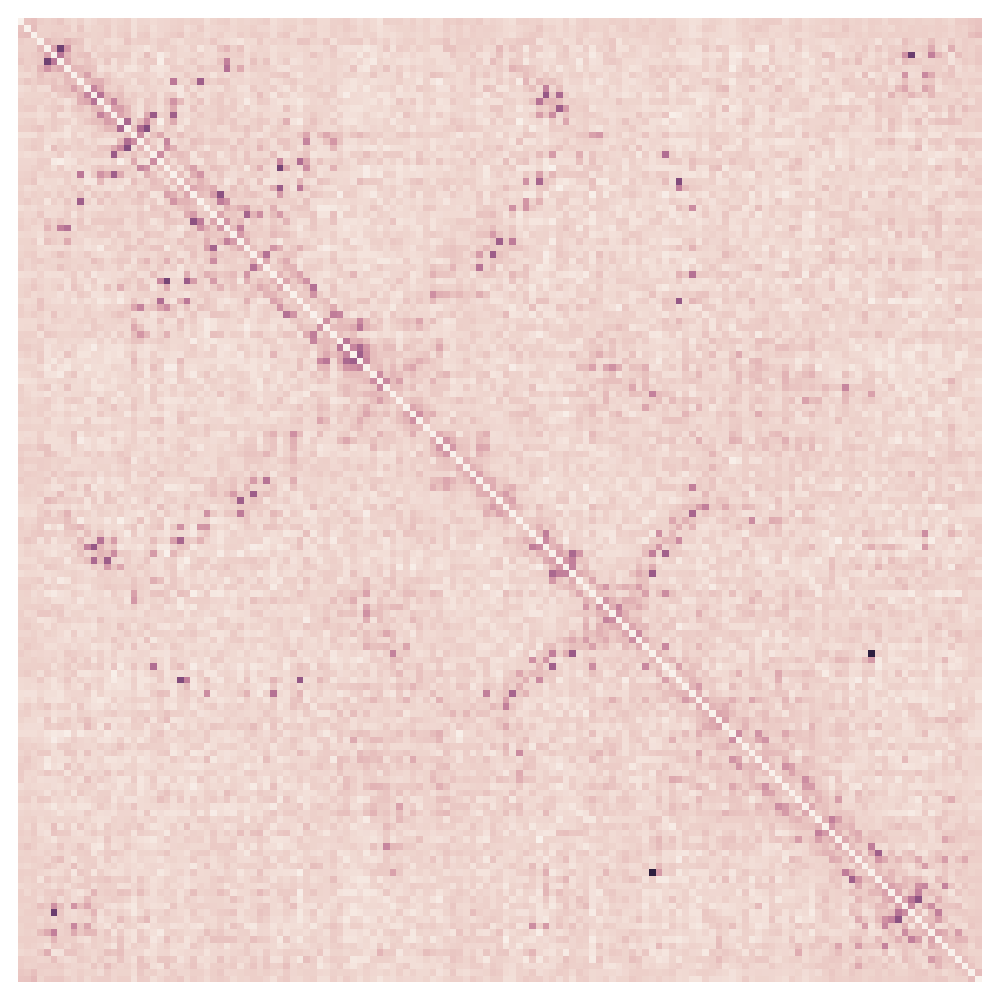
Performance measurements
Accuracy : Predictions that are correct :
Specificity : Non-contacts identified :
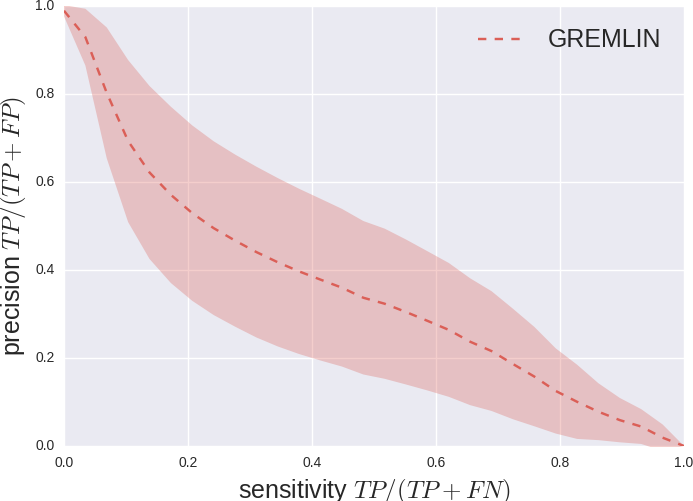
Precision : Contacts identified that are true :
Sensitivity : True contacts identified :
ROC curves measure Sensitivity vs Specificity.
False positives (FP) are worse than false negatives (FN).
We measure Precision vs Sensitivity.
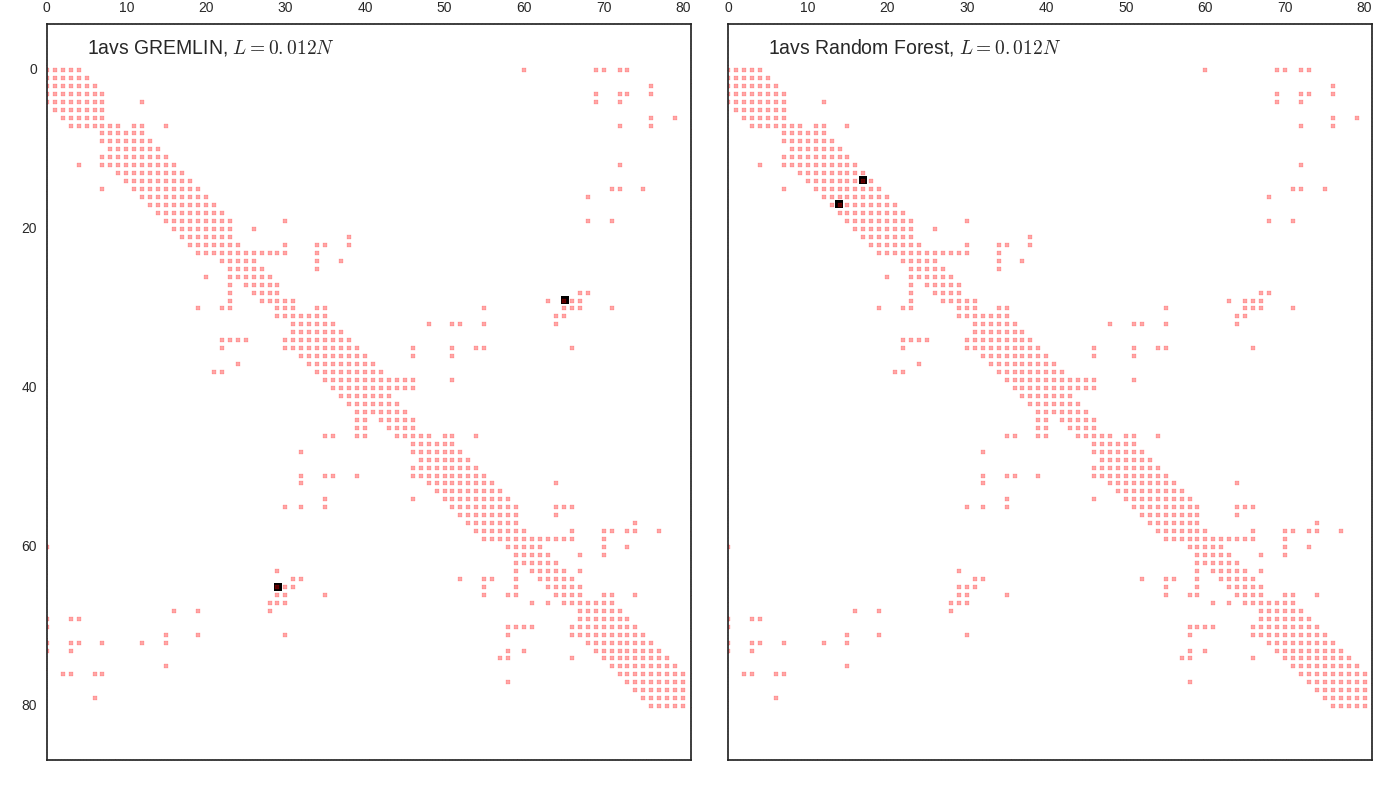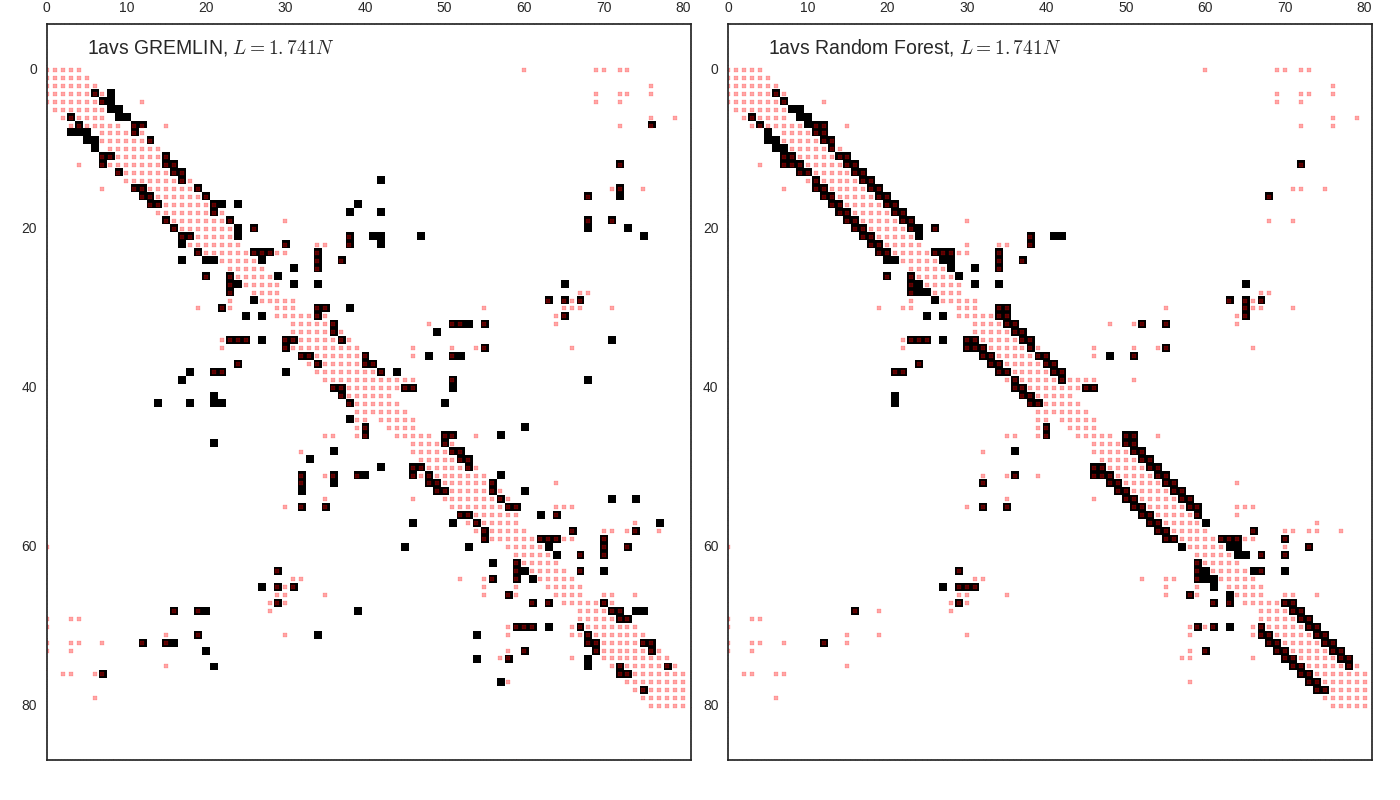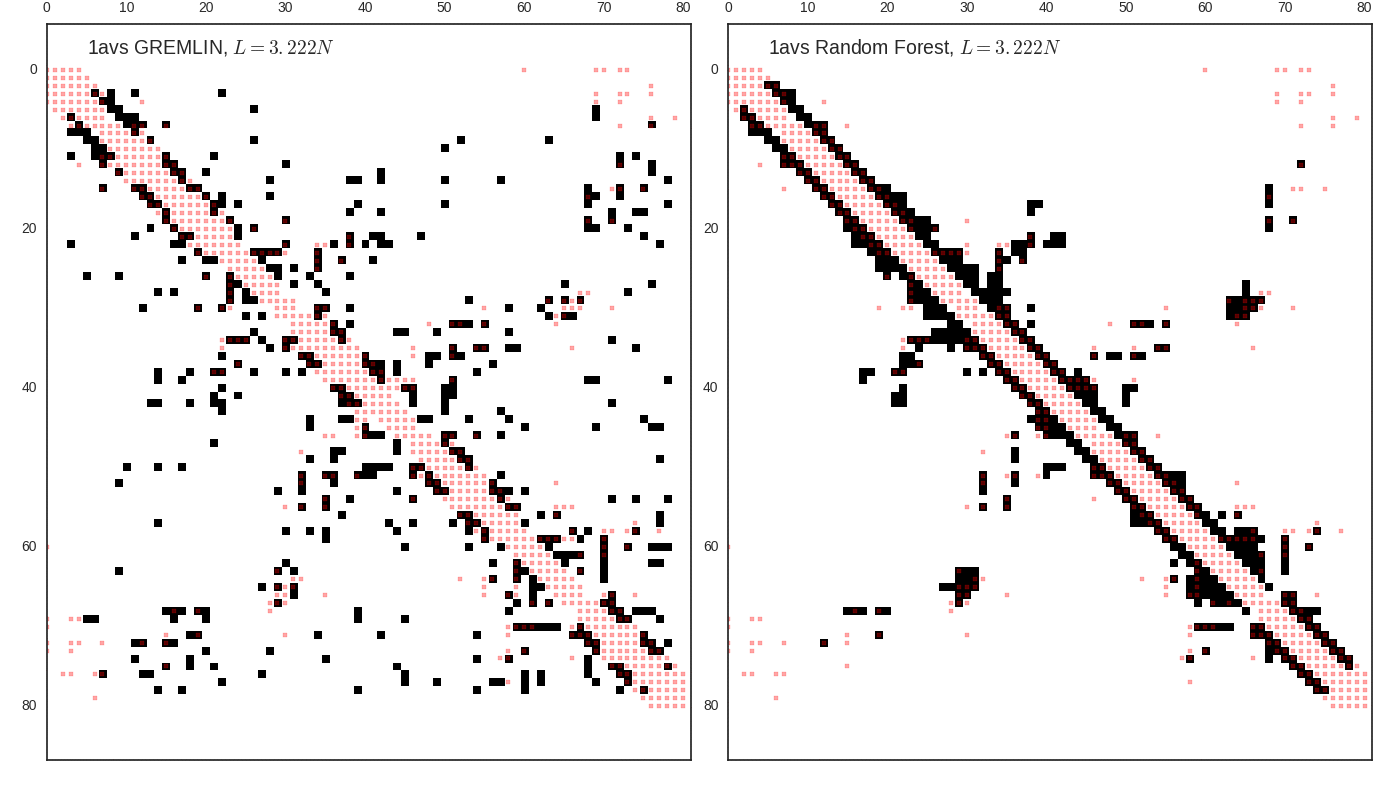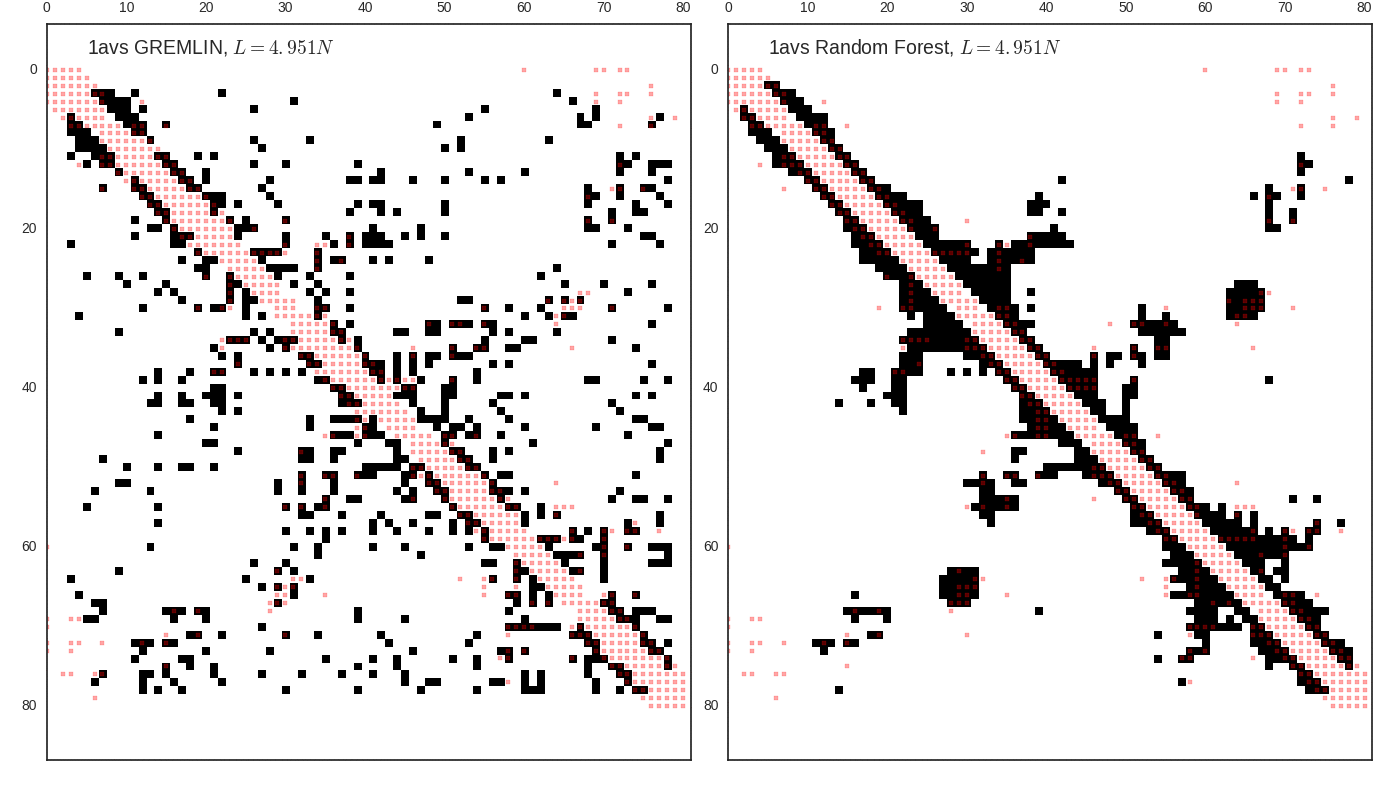
GREMLIN Predictions
Hypothesis:
Local structure can enhance contact prediction.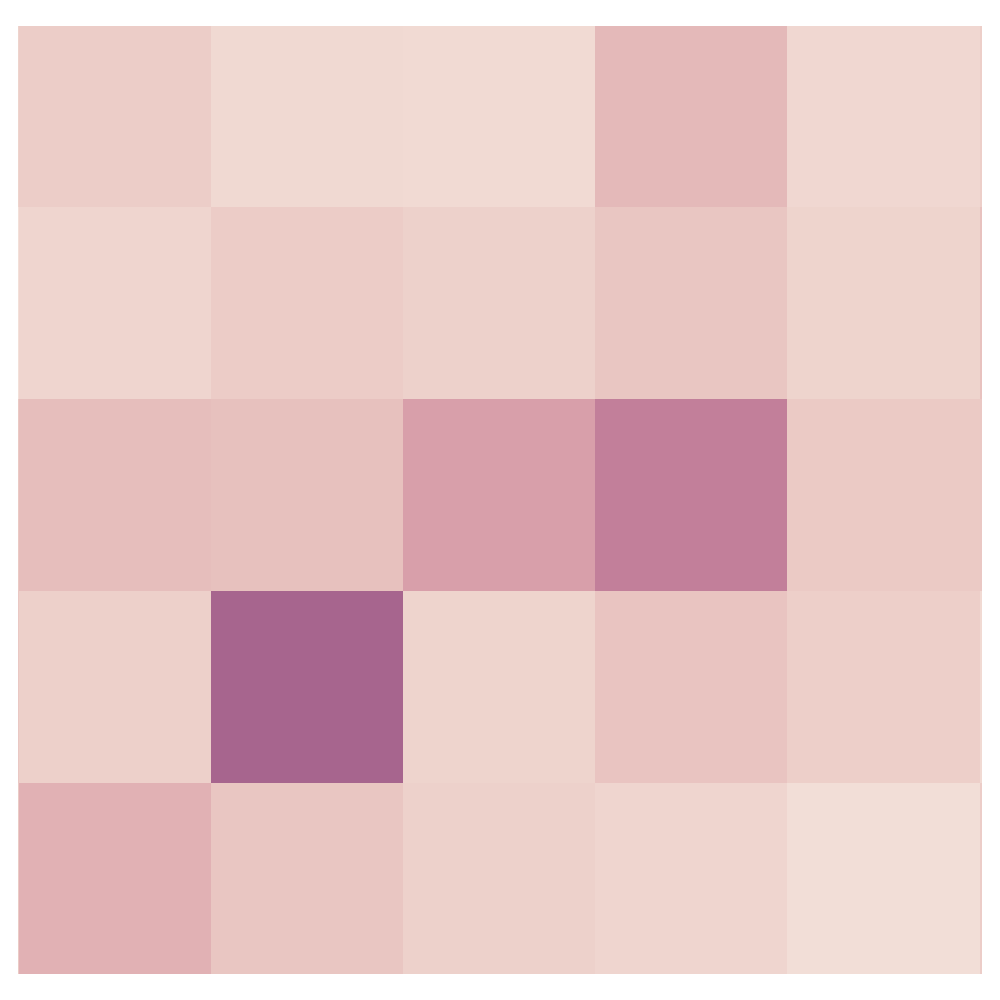
Secondary structure is local (helices, sheets, turns).
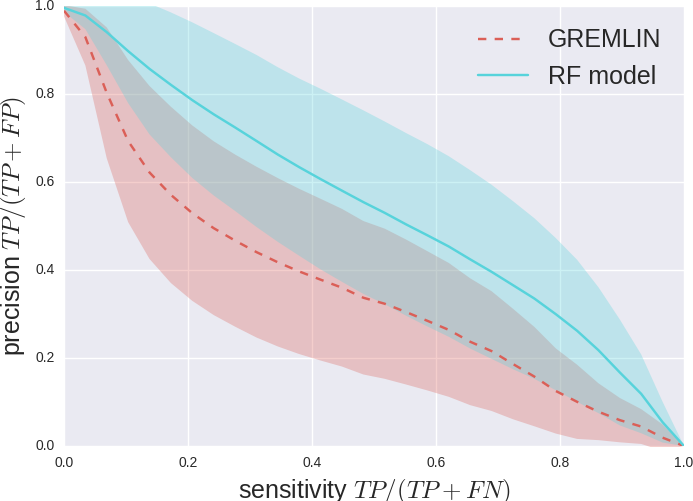
Random forest (RF) score model
Machine learn local pixel maps for contact/non-contact.Normalize data: subtract mean, scale to unit variance.
Train with extremely random forests*, variant with dropout.
(e)RF's were more robust than traditional shallow learning like SVM.
kernel_window=2, n_trees=200, ratio_TP_to_TN=20
What are Random Forests?
Decision trees are good for simple data, but tend to overfit.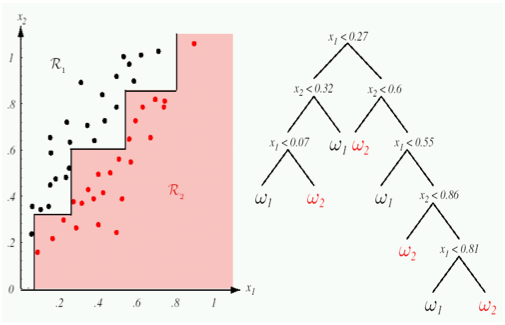
Random forests are multiple decision trees with 1] "random splits",
2] selective subsets, (each tree only gets to see a subset of the data).
This increases individual bias but the average corrects for overfitting.
Improved RF model Predictions
Contact map vs cutoff length (1a3a)
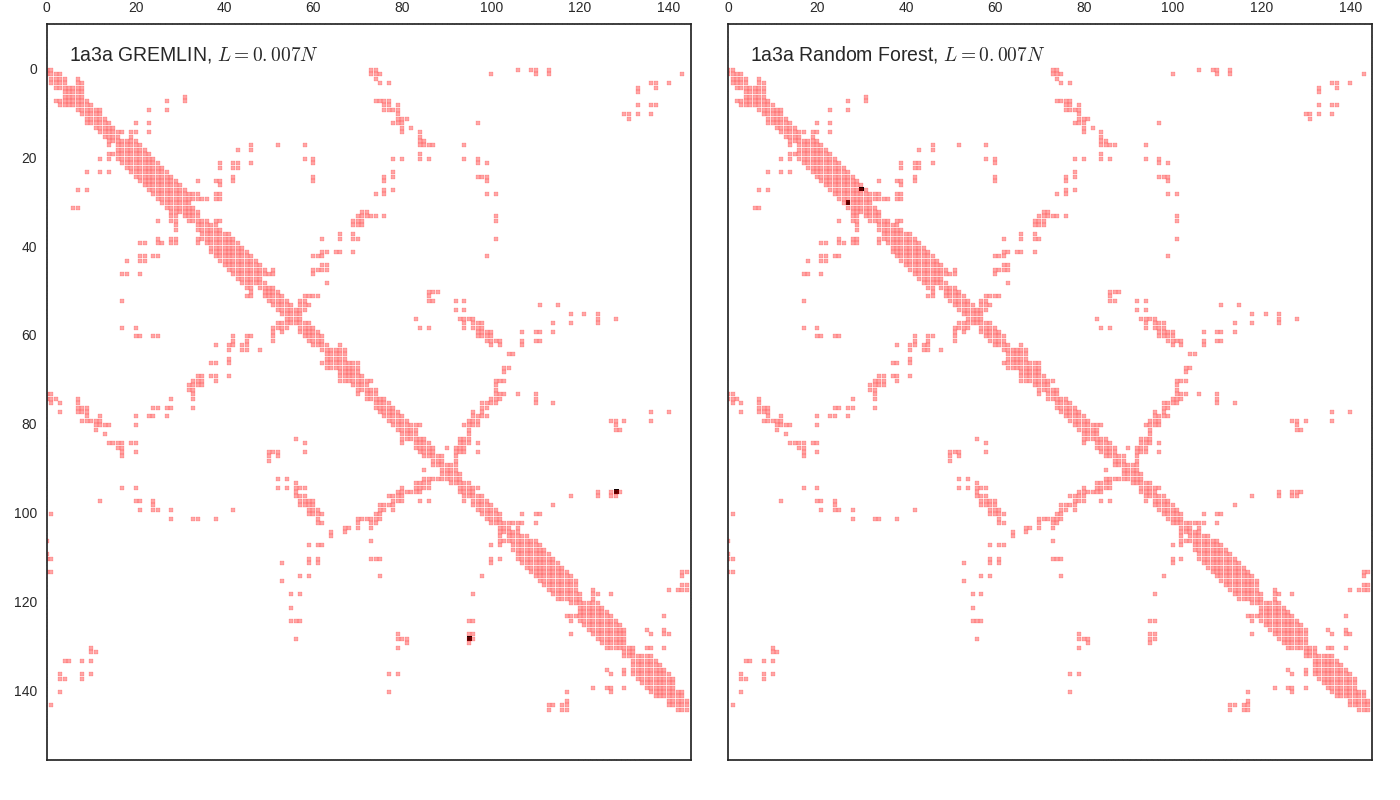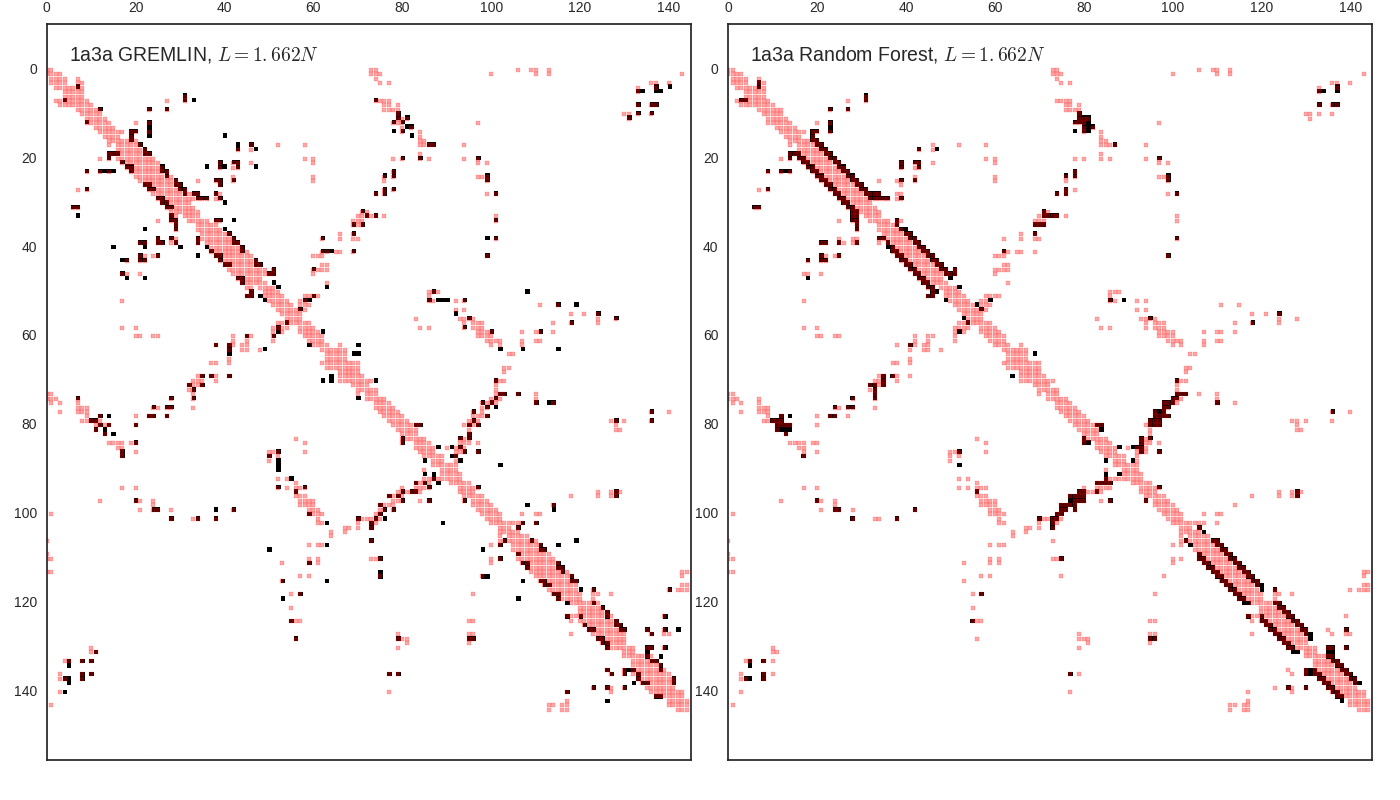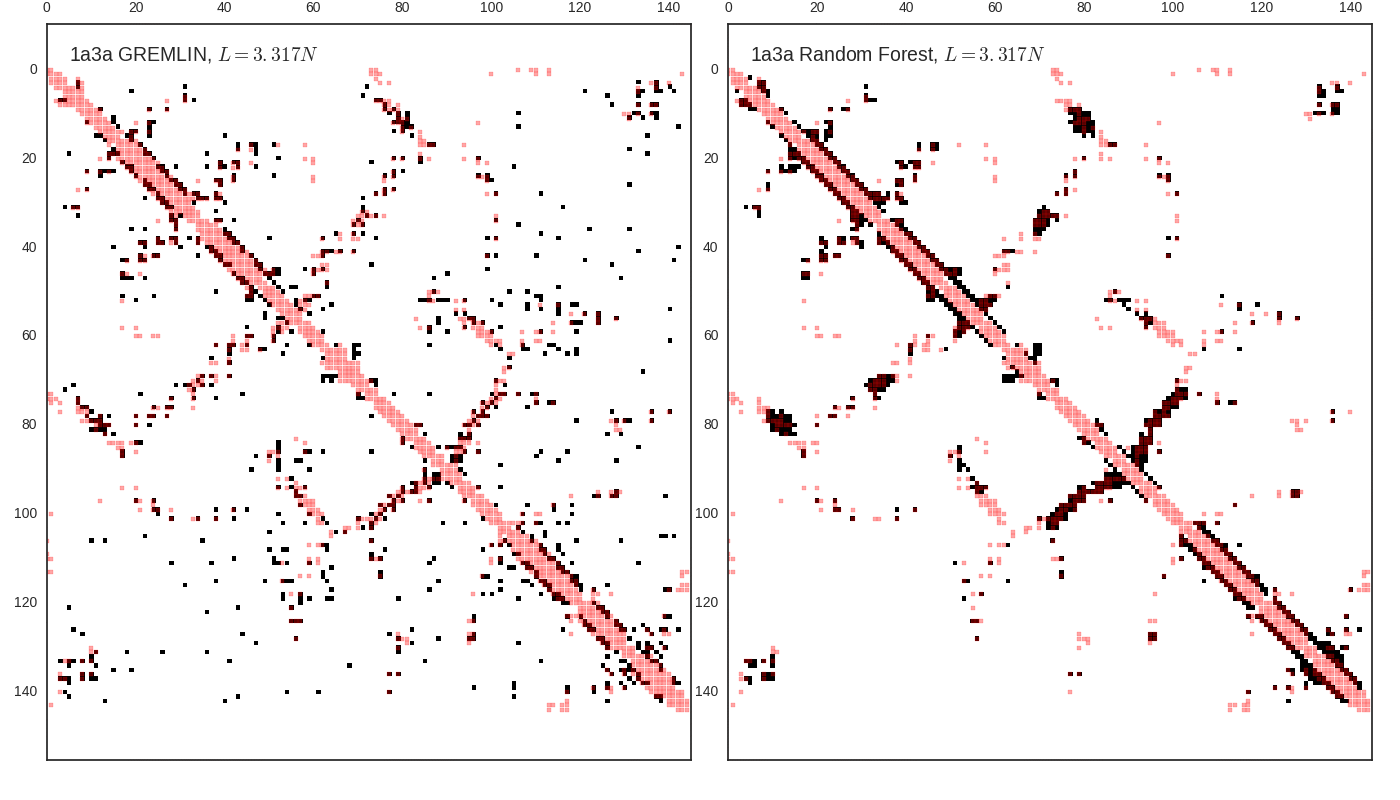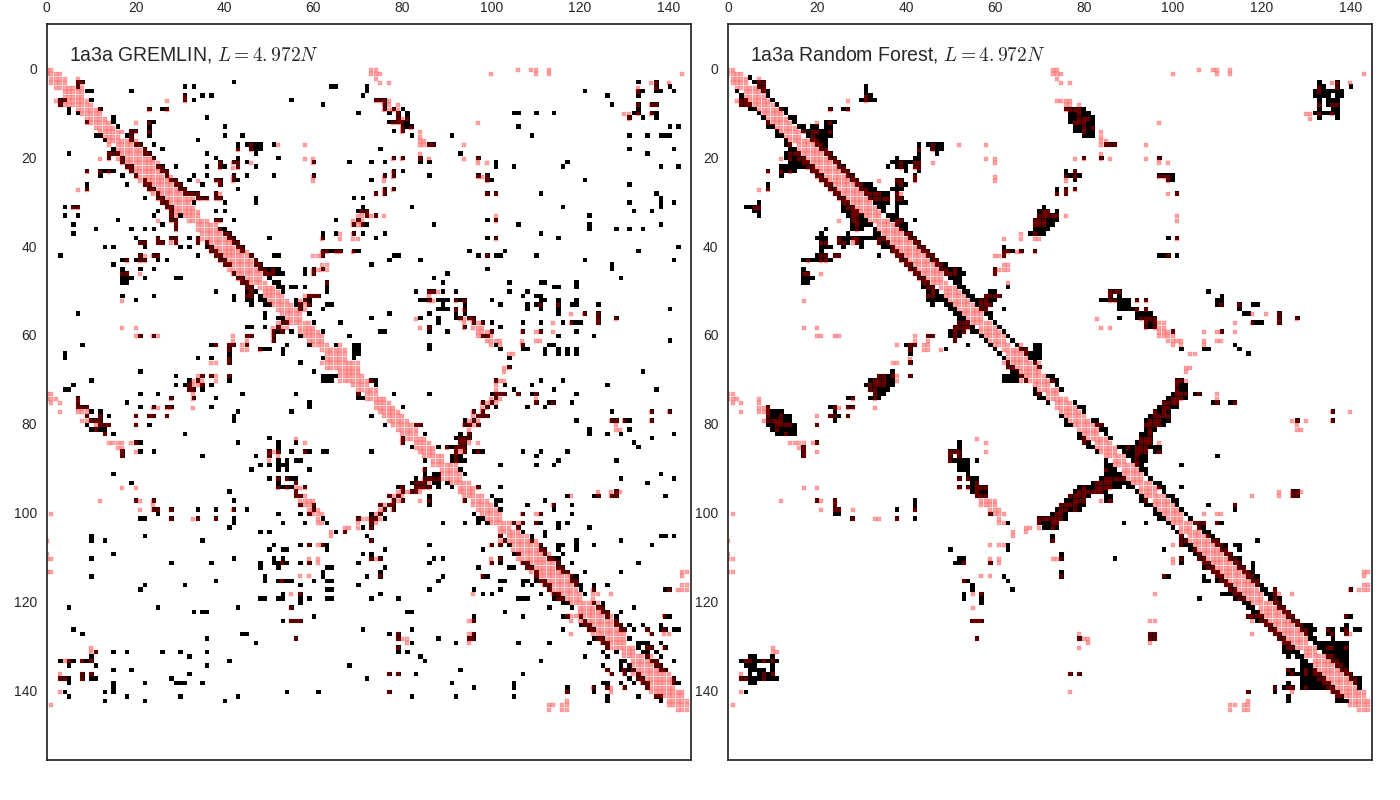
Contact map vs cutoff length (1avs)
Folding simulations
coarse-grained MD simulationUnbiased estimate of contact map fold.
No prior knowledge (ROSETTA fragments, SS pred., etc...).
Potential = Backbone + smoothed well with range ~ .
Rapid collapse to contact potential
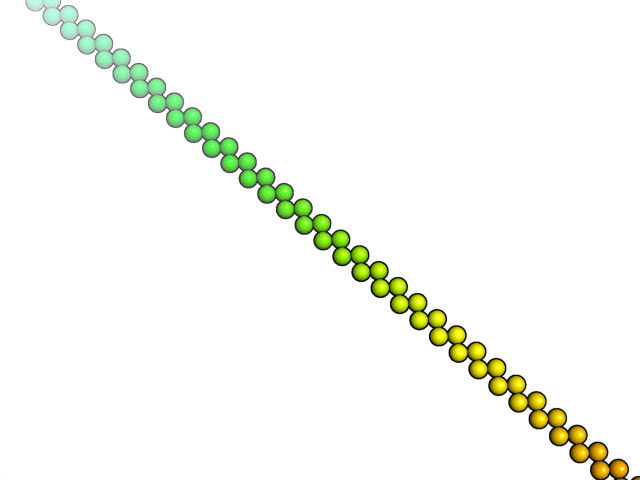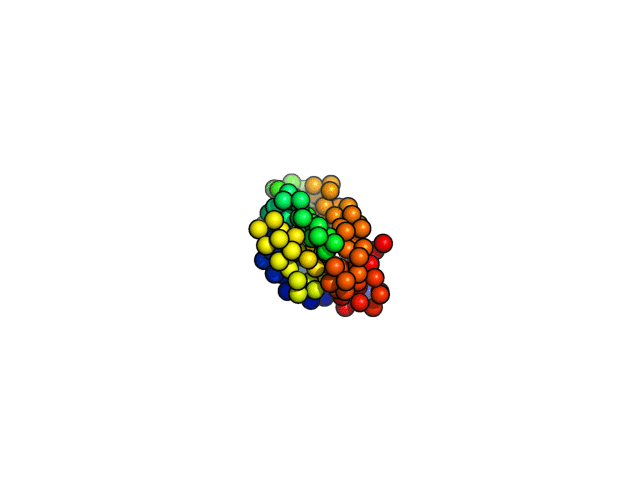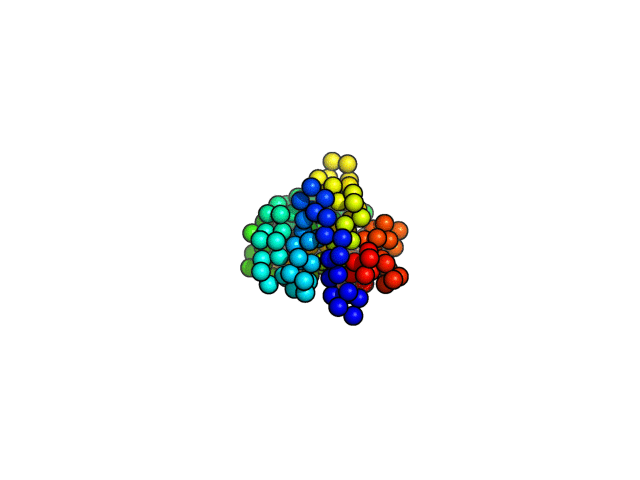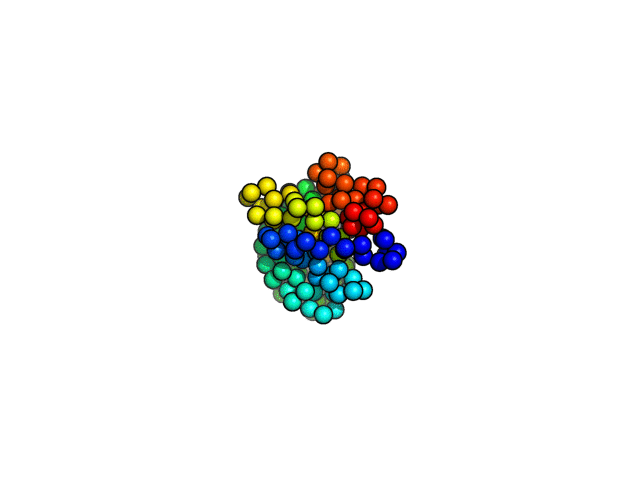
coarse-grained MD simulations
Folding simulations,
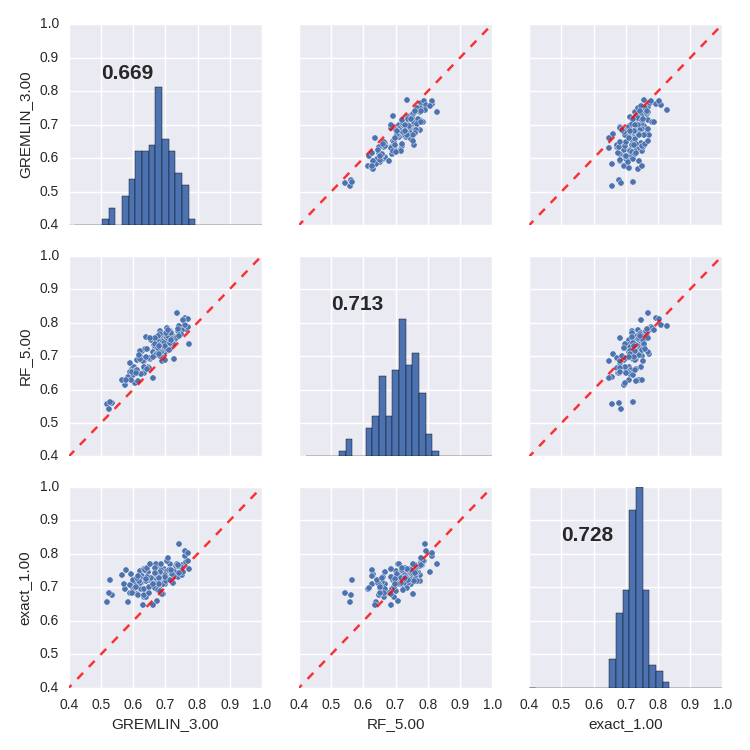
Features of the RF model
scientific insight beyond predictive capability
Predicted contacts are closer to true contacts
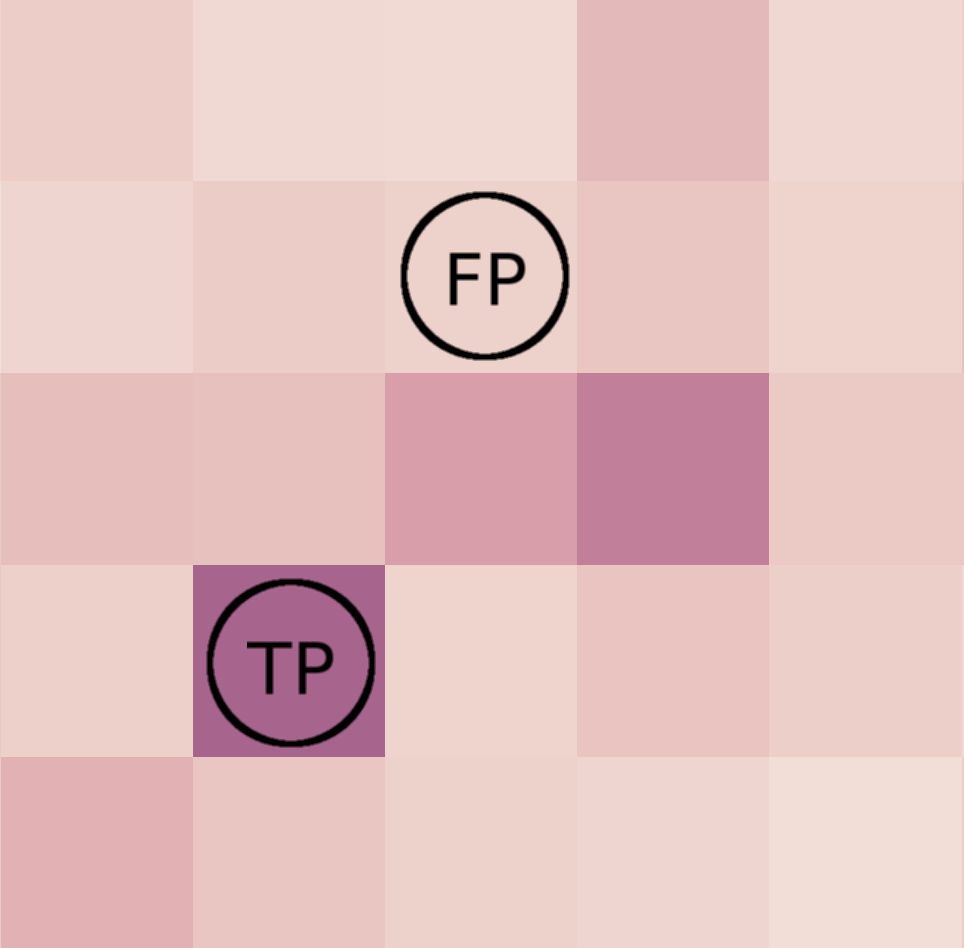
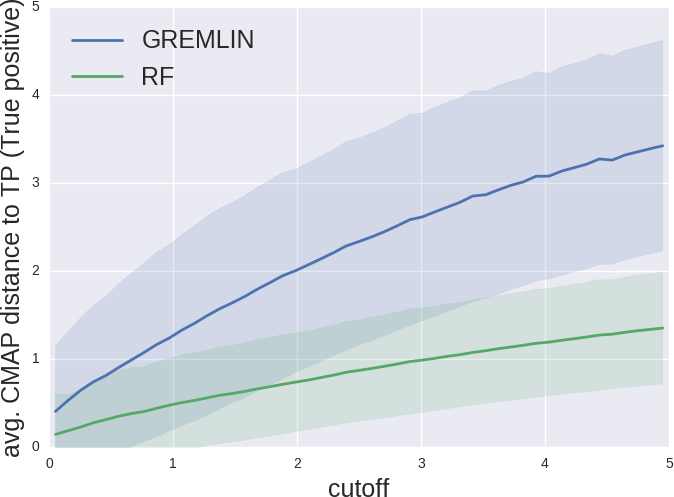
Improvement in folding
In potential, more contacts better RF fold.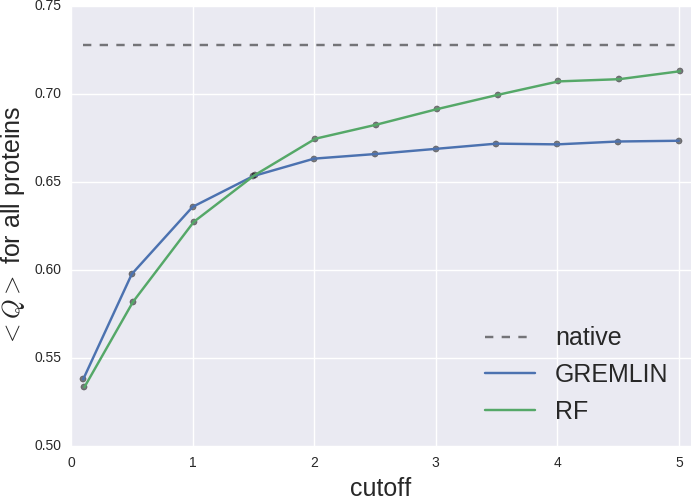
Random Forest features (central difference most important)
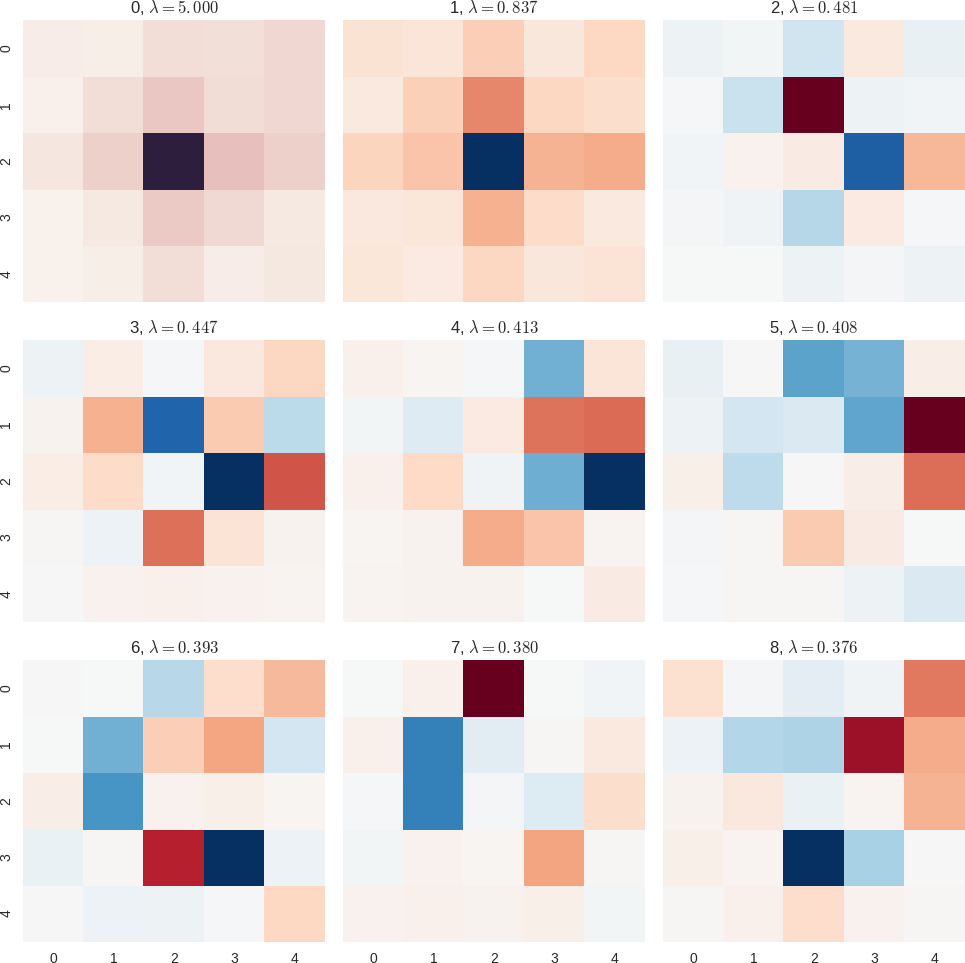
Future work & Extensions
Convolutional neural networks to improve prediction:
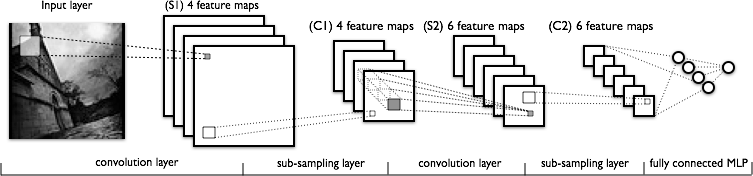
can be used as an effective Hamiltonian for evolutionary movement.
Future work & Extensions
Enhanced structure prediction, ROSETTA et. al.
Disambiguation of intra/inter predictions.
Estimation of binding partners and hetrodimers from .
Thanks, you.
Robert Best (NIH/NIDDK)
Wenwei ZhengTravis Hoppe
Pengfei Tian
Jan Domanski
Mathias Bellaiche